Insight Hub
Stay updated with the latest trends and insights.
Charged Up: The Surprising Secrets of Electric Cars
Discover the shocking truths behind electric cars that will change how you think about driving. Get charged up with our surprising insights!
How Electric Cars Work: Unpacking the Technology Behind the Charge
Electric cars operate using a combination of complex technology and innovative engineering that sets them apart from traditional gasoline vehicles. At the core of an electric car is its battery, which stores electricity used to power an electric motor. Unlike internal combustion engines that convert fuel into mechanical energy, electric vehicles (EVs) convert stored electrical energy into power to drive the wheels. This technology results in increased energy efficiency, as electric cars typically convert over 60% of the electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels, in contrast to conventional gasoline vehicles, which only convert about 20% of the energy stored in gasoline into motion.
Key components of an electric car include the battery management system, electric motor, and charging system. The battery management system monitors the state of the battery, ensuring safety and optimal performance. The electric motor, which can be either AC or DC, drives the wheels instead of using a complex gearbox. Charging is another critical aspect, with most EVs utilizing Level 2 (240V) chargers for home use and public fast chargers providing higher voltage for rapid charging. Overall, the synergy of these components allows electric cars to deliver a smoother, quieter driving experience while minimizing environmental impact.
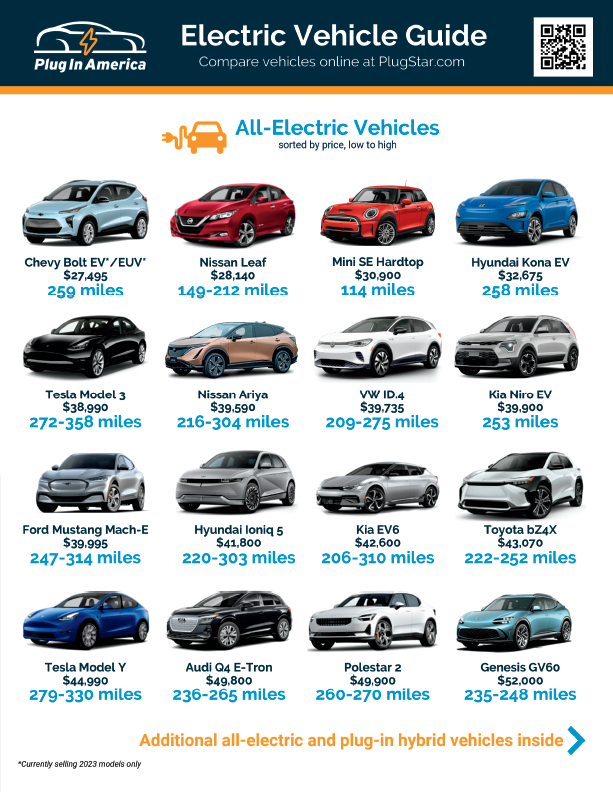
The Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles: Myths and Facts
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a heated debate about their environmental impact. While proponents tout their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, critics highlight the carbon footprint associated with battery production and electricity generation. One common myth is that EVs are completely emission-free. In reality, the environmental benefits depend significantly on the energy sources used in electricity generation. For instance, in regions that rely heavily on coal, the emissions associated with charging EVs may diminish their overall benefits. However, as renewable energy sources like wind and solar become more prevalent, the lifecycle emissions of electric vehicles are likely to decrease significantly.
Another prevalent misconception is that the production of electric vehicle batteries is more harmful than traditional car manufacturing. While it is true that the extraction of lithium and other materials for batteries poses environmental challenges, many facts can counter this narrative. Firstly, EVs tend to have a longer operational life, leading to reduced emissions over time compared to internal combustion engines. Additionally, advancements in battery recycling technology are improving the sustainability of battery production. According to some estimates, the environmental impact of electric vehicles could be 70% lower over their lifetime than that of conventional vehicles when considering their full lifecycle emissions. This makes them a crucial part of the transition towards a more sustainable future.
What You Need to Know About EV Battery Life and Maintenance
Understanding EV battery life is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of your electric vehicle. Most electric vehicle batteries are designed to last between 8 to 15 years, depending on usage, climate, and charging habits. Regularly monitoring the state of charge (SOC) is crucial; keeping your battery between 20% and 80% state of charge can greatly enhance its lifespan. Additionally, extreme temperatures can affect battery efficiency, so it's advisable to park in shaded or temperature-controlled environments whenever possible.
Proper maintenance of your EV battery can significantly influence its durability. Always use the manufacturer's recommended charging equipment to minimize the risk of damage. It's also beneficial to employ the following practices:
- Schedule regular inspections to check for any signs of wear or degradation.
- Utilize regenerative braking when possible to conserve energy.
- Avoid leaving your vehicle fully charged or completely depleted for extended periods.