Insight Hub
Stay updated with the latest trends and insights.
RFID: The Invisible Thread Connecting Your World
Discover how RFID technology weaves through everyday life, enhancing convenience and security. Uncover its fascinating impact on our world!
Understanding RFID Technology: How It Works and Its Impact on Everyday Life
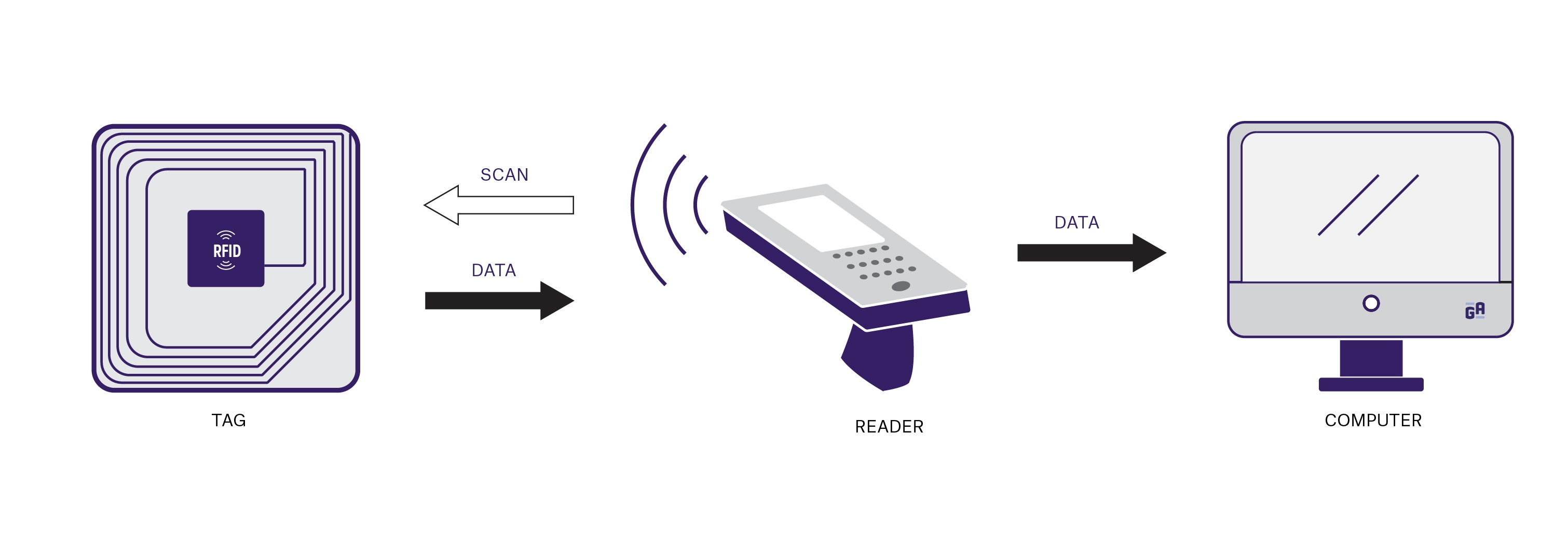
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has revolutionized the way we track and manage items in various industries. At its core, RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Each RFID tag contains a microchip and an antenna, allowing it to communicate with an RFID reader. This seamless communication enables real-time data exchange, which is invaluable for inventory management, supply chain logistics, and asset tracking. Unlike traditional barcode systems that require line-of-sight scanning, RFID can operate at greater distances and even through obstructions, making it a superior choice for many applications.
The impact of RFID technology on everyday life is profound and far-reaching. From retail stores that utilize RFID for efficient inventory management to healthcare facilities that ensure patient safety and accurate medication distribution, the benefits are clear. For consumers, RFID enhances the shopping experience by streamlining checkout processes and reducing wait times. Additionally, as more everyday items integrate RFID, such as clothing and personal belongings, individuals can expect increased convenience and security, ultimately leading to a more connected and efficient world. As we continue to explore the possibilities of this technology, it is evident that RFID will play a significant role in shaping our future.
Counter-Strike is a popular first-person shooter game that has been a staple in the competitive gaming community since its release. The game pits teams of terrorists against counter-terrorists in various game modes, where strategy, teamwork, and skill are crucial for success. Players can choose from a range of weapons and tactics to outsmart their opponents in fast-paced matches.
For those looking for gadgets beyond gaming, you might want to check out the Top 10 Alternatives to Bluetooth Trackers which offer various tracking solutions.
The Future of Inventory Management: Leveraging RFID for Efficiency
The future of inventory management is being reshaped by innovative technologies, and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) stands at the forefront of this transformation. By replacing traditional barcode systems, RFID enables real-time tracking of inventory items without the need for direct line-of-sight scanning. This leap in technology not only enhances accuracy but also significantly reduces labor costs associated with manual inventory checks. As businesses strive for efficiency, implementing RFID systems can streamline operations, minimize stock discrepancies, and ultimately lead to improved customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, the integration of RFID technology into inventory management processes allows for better data collection and analytics. Businesses can leverage the insights gained from RFID data to forecast demand more accurately, manage stock levels effectively, and optimize supply chain logistics. According to industry experts, companies that adopt RFID are expected to see a 20%-30% reduction in carrying costs and an increase in inventory turnover rates. As we look to the future, it’s clear that RFID will play a crucial role in driving efficiency and fostering innovation within the field of inventory management.
What Are the Security Risks of RFID and How Can You Protect Yourself?
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized the way we track and manage assets, but it also introduces significant security risks. One of the primary concerns is the potential for unauthorized scanning of RFID tags, which can expose sensitive data such as personal identification and payment information. Hackers can utilize RFID readers to gain access to this information without the victim's knowledge, a method commonly referred to as eavesdropping. Additionally, the risk of relay attacks, where an attacker amplifies the signal from an RFID tag to gain access to secure locations or devices, is a growing concern.
To protect yourself from these security threats, consider implementing the following measures:
- Use RFID-blocking wallets or sleeves that prevent unauthorized scanning.
- Disable RFID features on your devices, if possible, especially when not in use.
- Monitor your accounts regularly for any suspicious activity, and report it immediately.